
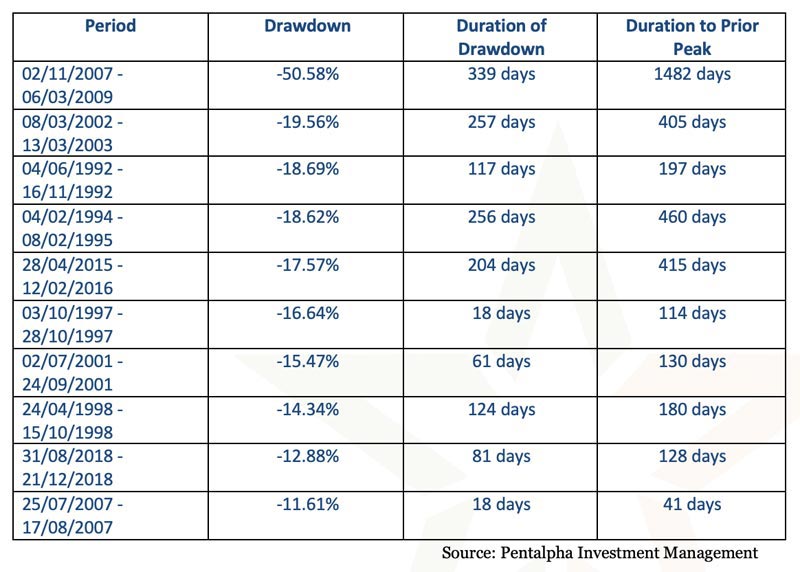
Chen ( 2009) specifically aims to predict the bear markets using the set of macro variables as leading indicators, and finds that the portfolios actively managed using the signals from the inverted yield curve and inflation significantly outperform the passive buy-and-hold portfolios. Obviously, the ability to predict a recession is the foundation of the global macro strategy.Īcademic literature provides overwhelming evidence that an inverted yield curve has been significant in predicting the past recession (for example Estrella and Mishkin 1996), and that recessions are associated with the major stock market downturns or bear markets (Campbell 1987 Dladla and Malikane 2019). Guided by the historical stock market cycles, the global macro longer-term investing strategy is simple-reduce (or eliminate) equity exposure before a recessionary bear market, and increase equity exposure at a depth of a recession with expectations of a new growth cycle. Unlike the systematic rule-based strategies, the discretionary global macro strategy retains the discretion and flexibility in decision-making when evaluating the macro environment, with being less reliant on purely empirical and statistical analysis. Global macro strategy, which is a subset of hedge fund strategies, considerers the various systematic macro variables (monetary policy, fiscal policy, political, geopolitical, and other systematic events) to make cross-asset allocations and directional trades. What explains the depth of a stock market drawdown? This article aims to answer this question from the discretionary global macro strategy perspective.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
